The IoT solutions in healthcare sector are increasingly being implemented and changing the way patients are treated. From smart home gadgets that help monitor elderly patients to edge computing in healthcare used in the processing of data, IoT and remote patient monitoring is defining the future of healthcare. This paper discusses the effect of IoT and Edge Computing in healthcare to come up with the challenges and benefits of these smart technologies.
If we take a look at demographic changes, we can see that the global population is aging. Some forecasts say that by the year 2050, the proportion of the world’s population over age 65 will double. For people who are elderly or with disabilities, smart home healthcare devices are not just a novelty but can become a necessity and can be used as assistive technology, providing more functional capabilities and independence. This means that more and more people will need additional care at their homes. Considering different highly secure healthcare IoT services for people who wish to remain independent and live in their own homes is a must. This assumes that we would also need to share more personal – health-related data with our doctors, hospitals, and emergency services.
The large diversity of needs in a home-based patient population requires complex technology, more regulations, and a high level of cybersecurity. Together with universities and industrial partners, we are focusing on building a strong competence network to bring many benefits that will promote Europe’s digital sovereignty, boost security, and improve quality of life. Let’s think about our future and improve Europe’s cybersecurity on all levels!
Cybersecurity Challenges in Using IoT in Healthcare
As we move towards a future where smart homes become more prevalent, we must address the cybersecurity challenges associated with these innovations. Innovation means different things to different people, depending on the context in which it is being reviewed. We will review the emerging concept for new values for cybersecurity in Europe by focusing on the future of smart home healthcare and its potential.
The smart home is not a new concept; in fact, the smart medical home for seniors, including detecting falls, was discussed in the late 1990s to early 2000s. As in all new technologies that are rising, smart home IoT devices will take time to catch on. With more devices they are more and more security issues to be considered in our homes. By buying different devices, we usually do not think about the security of the data we are providing when installing devices in our own homes or creating accounts and sending data to “someone’s” cloud.
“At the end of the day, the goals are simple: safety and security.” – by Jodi Rell
we should have this phrase always on the mind.
Why is Europe’s Cybersecurity Shield a must for your Smart Home?
There are lively discussions currently happening around the world where security should reside; at the device or cloud level. Now, for the majority of connected consumer products, it is in neither. Anyone can buy devices and play around by programming them to turn on lights, detect movements in the house, and similar, but what about the security of these data? We need to consider moving the regulations and security of smart home IoT devices to another level by building a European cyber-shield. More secure and digital Europe is needed!
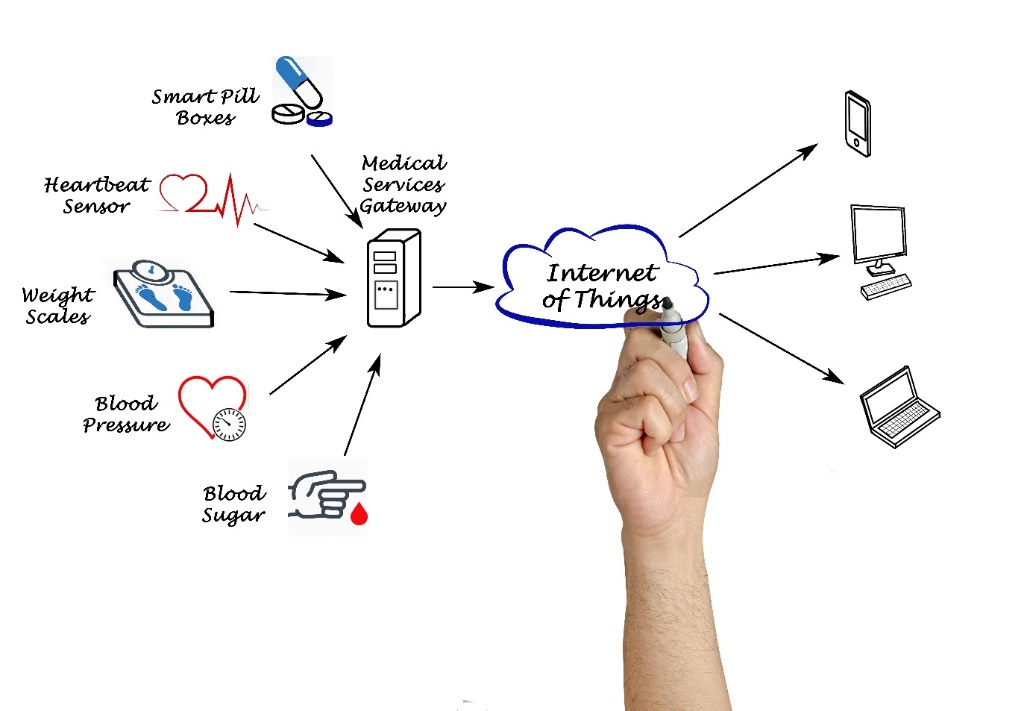
Patient Profile for Remote Patient Monitoring Services
The development of IoT in healthcare affects the management of patient’s data and remote patient monitoring devices. Effective and appropriate treatments, procedures, and many activities that take place within the healthcare systems are anchored on the right identification of the patient. In what way can one guarantee that the right patient information is available and that the patient gets the right treatment? How can IoT solutions assist the doctors and assist in patient’s health check up at home?
Patient Profile Coming from the Fridge?
Smart IoT devices and consumer IoT services are more frequently used in homes and personal lives, and help users to be more aware of their health status. For instance, a smart fridge can ascertain whether the user purchases fresh food often and a smartwatch can track the user’s exercise frequency. This information assists in building up of a healthy habits profile which enhances the quality of life of the user.
Regarding the above and within the scope of the Concordia project, we aimed at identifying the existing consumer IoT medical solutions, interacting with them in the home area network, storing the collected data, and transferring it to doctors and hospitals. Combining the health related data with other parameters collected from the fitness trackers, remote patient monitoring services can help doctors provide the best treatment.
How to Identify Patients at Home?
Patient identification is a critical topic in the healthcare process as there could be significant consequences if a mistake occurred. Wrong medication, transfusion, testing, or procedures, which can harm or threaten a patient’s health or life, are caused by failure to correctly identify patients. One of the considerable challenges we have been investigating in the Concordia project is the way to identify patients at home as well as to share patient data with doctors or hospitals. Since society ages, more and more patients are needing medical care in the home area. Therefore, it is important to assure that patients’ data are securely stored, securely shared with doctors or nursing centers, and that patient digital identification is secured.
As a part of the digital identity of the patients in the e-health pilot of the project Concordia and due to the worldwide pandemic caused by the Covid-19 virus, vaccination certificates are considered together with patient health cards for patient identification.
The large diversity of needs in a home-based patient population requires complex technology, more regulations, and a high level of cybersecurity, especially for patient identification. Together with universities and industrial partners, we are focusing on building a strong competence network to bring many benefits that will promote Europe’s digital sovereignty, boost security, and improve quality of life.
How Edge Computing is Transforming Healthcare?
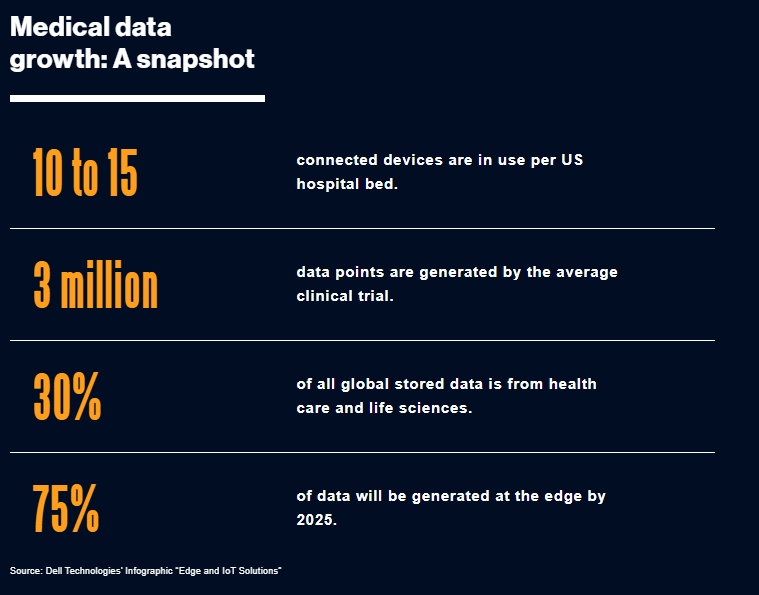
Edge computing in healthcare is another revolutionary advancement that is revolutionizing healthcare through enhancing data analysis and storage. data processing at the edge of the network or directly at the devices used in the clinic, hospital, or even directly on the patient’s device outside of clinical environments helps to analyze and collect data as well as accelerate and enhance the accuracy of the diagnoses by bringing big data processing and storage closer to the source. Security and high-level virtualization are important in these systems because they have to provide dependable and predictable process execution. Moreover, the information that can be identified with patients or other sensitive information must also be safeguarded from disclosure.
Medical applications and IoT healthcare devices are one of the most critical categories of systems. The use of these applications in the cloud is considered as unsafe because it involves patient data. Edge computing can effectively minimize the amount of data that needs to be exchanged between the patient and the healthcare provider. Edge processing can also help to limit the data that is transmitted to the healthcare providers thus lowering the cost and the strain on bandwidth. All this allows for early and quicker identification and treatment of the patients, hence improving the overall treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Benefits of Edge Computing in Healthcare Diagnostics
Due to the recent developments in technology, it is now possible to produce large volumes of data. There is a constant demand for the transfer of this data faster and more securely to avoid its interception by unauthorized persons. Edge computing can be defined as the enhancement of data transfer rates by utilizing the speed of the fifth generation (5G) communication to transfer data with less latency and high bandwidth. This would greatly assist in the enhancement of acquiring quick and faster response from healthcare entities. Decreasing the transmission of the data can help minimize the risk of interception by cybercriminals. Consequently, Edge computing can help achieve the best levels of medical privacy together with adherence to the laws and standards.
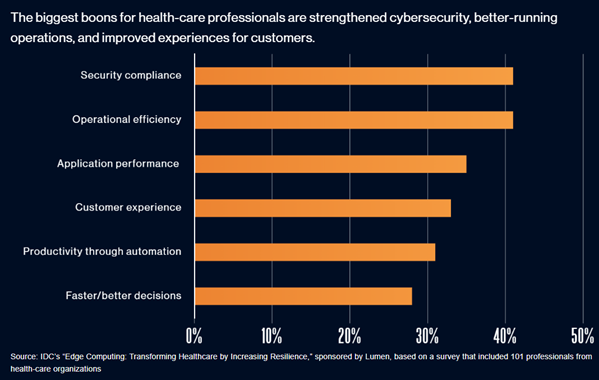
Impact of Edge Computing on Healthcare Data Security
The use of digital health data is growing while the threat of cyberattacks and data breaches also rises. There are several technical measures that need to be taken in this regard in an effort to prevent the medical data from being exposed. One of the possible solutions described by ENISA is the use of pseudonymization.
These technologies such as big data, AI and edge processing are making their way into the healthcare sector. With the advances in medical technologies of the future, diagnosis and treatment by paramedics will be quicker and more precise. Additionally, Edge computing in healthcare can help doctors in their work or even perform some of the work that they do. Therefore, all kinds of cybersecurity threats should be countered and the issue of patient data security should be further developed. Altogether with universities and industrial partners, eesy innovation is working on the development of a strong competence network for the provision of benefits that will enhance the digital autonomy of Europe, increase safety, and enhance the quality of life.
Conclusion
With the advancement of IoT and edge computing in healthcare, the healthcare industry is set to experience a revolution in the management of patients, operations, and most importantly, data protection. But with these advancements come certain difficulties, especially in terms of security and patient information. With these challenges in mind and the right approach and technologies, it is possible to build a future in which healthcare is more accessible, individualized, and secure. The use of smart home technologies, remote patient monitoring devices and the use of Edge computing in healthcare not only indicates how patient care could be transformed in the future but also underlines that there is still a lot of work to be done in the field of protecting sensitive health related information.
FAQ
What are the essential elements of Remote Patient Monitoring Services?
The primary equipment usually consists of wireless sensors that are capable of monitoring various physiological parameters, including ECG, blood pressure, blood glucose, weight, SpO2, and heart rate. Some of the examples of RPM devices include blood glucose meters and the use of remote physiologic monitoring services assist in aggregating and storing such data in databases to support patient education and improved health outcomes.
What is the most common form of remote patient monitoring?
The most common form of remote patient monitoring is the home monitoring program, which employs the use of different gadgets to monitor patients from a distance. This can be useful for healthcare research and quality since it offers data on patients’ condition in the everyday world. Furthermore, the application of devices in remote monitoring is helpful in increasing patient compliance to the recommended treatment regimens as well as enable the healthcare provider to step in when the patient is not following the recommended schedule. Moreover, the effective RPM program enhances patient care beyond the healthcare facilities, addressing a vast population and providing holistic and individualized care.
What diseases can be monitored with the help of RPM devices?
There are many different types of chronic conditions that can be managed through RPM and the list is constantly expanding. Some of the diseases that are usually monitored with RPM devices include hypertension, diabetes, congestive heart failure, COPD, hypertension, pneumonia, and post-surgical patients.
Who can use remote patient monitoring (RPM)?
Due to the increase in the use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic, more patients can receive healthcare through RPM devices. In 2021, the CMS issued a final rule that practitioners may provide RPM services to remotely collect and analyze physiologic data from established patients if the monitoring is reasonable and medically necessary and “used to develop and manage a treatment plan related to a chronic and/or acute health illness or condition.”